EcoHAT遥感水文站简介
杨胜天 娄和震 赵长森等
北京师范大学 水科学研究院 遥感水文研究组
1、背景
河道流量,特别是序列的流量资料是表征水循环过程的重要指标,是水文循环过程中的积极因子,在区域水资源开发利用和河流生态保护中占有重要地位。但长期以来序列河川径流资料的获取途径都是通过建立水文站点进行人工观测,然而部分地区受制于多变的气候、崎岖的道路及恶劣的地理环境等不利因素,缺乏建立水文站的基础条件,成为广泛存在的水文资料匮乏区。
在此背景下,本项目组着眼于水文资料匮乏区径流获取困难的现实问题,结合该类地区水资源精细化管理的需求,基于具有自主知识产权的EcoHAT平台,探索利用无人机低空遥感数据、多源卫星遥感数据、水文模型共同构建水文资料匮乏区的流量估算模式,实现单点和序列的河川流量估算,同时建立了遥感水文站的线上共享系统,促进水文数据的共享共用。
2、遥感水文站基本原理与技术流程
以低空遥感数据的河道三维建模方法、野外数据采集试验、遥感流量估算方法和水文模型模拟分析为主要技术手段,以水文学原理、水力学和定量遥感等理论为基础,在IDL(Interactive Data Language)开发语言环境下建立EcoHAT_RS_RiverWidth、EcoHAT_UAV_RiverPara 和EcoHAT_RS_Flow遥感流量估算系统,并耦合在生态水文模型系统Eco-HAT中,具体技术路线如图1所示。
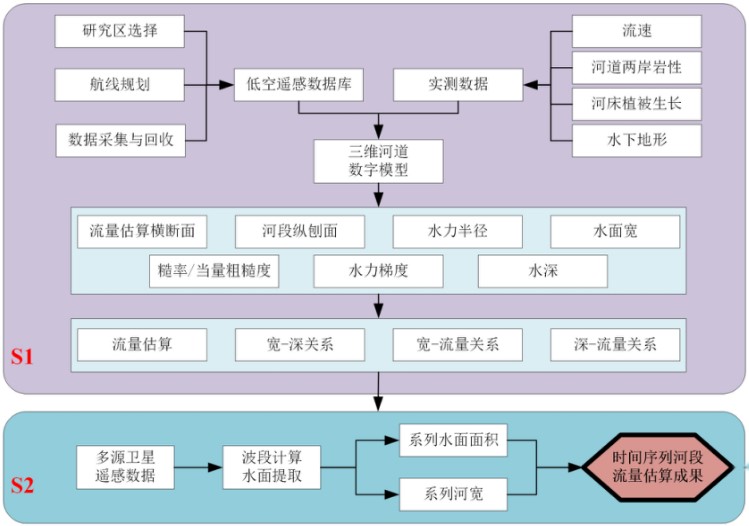
图1 遥感水文站基本原理与技术流程
3、监测结果指标与范围
流量估算所需关键参数(表1)主要通过以下五种方式获得:河流横断面、河段长度和水力梯度由低空遥感数据获取;水体指数NDWI由遥感影像提取获得;粗糙率是经验参数,其值取自统计表和实际测量;监测结果包括:水力半径、过流面积、河流宽度、水位、水深、流速和流量。监测河道包括大、中、小河流,以及灌渠小型水库等,河道(河谷)宽度为5m~500m,常规监测时间为月,可依据卫星过境时间实现实时监测,卫星空间分辨率为10米时,监测误差范围1%~10%。
表1 流量计算方法参数获取途径及分类
| 参数获取方法 |
参数 |
说明 |
| 经验值 |
n |
糙率 |
| 实测值 |
H |
水深 |
| 低空遥感 |
/ |
横断面 |
| L |
河段长度 |
|
| J |
水力梯度 |
|
| 高空遥感 |
NDWI |
水体指数 |
| 计算值 |
R |
水力半径 |
| W |
河流宽度 |
|
| A |
过流面积 |
|
| V |
流速 |
|
| Q |
流量 |
|
| h |
水位 |
4、全国EcoHAT遥感水文站分布情况
本项目组立足于水文资料匮乏区,依据遥感流量估算方法,目前在新疆艾比湖流域、吐哈盆地流域、疏勒河流域、青藏高原北部边缘地区、黄河上、中、下游流域、乌江流域内贵阳市周边喀斯特地区河流、湘江流域、苏南、苏北灌区、海河流域、长白山天池流域、密云水库上游流域、黑龙江三江平原河流及西藏金沙江上游河道共计建约500个遥感水文站,站点分布图见图2。
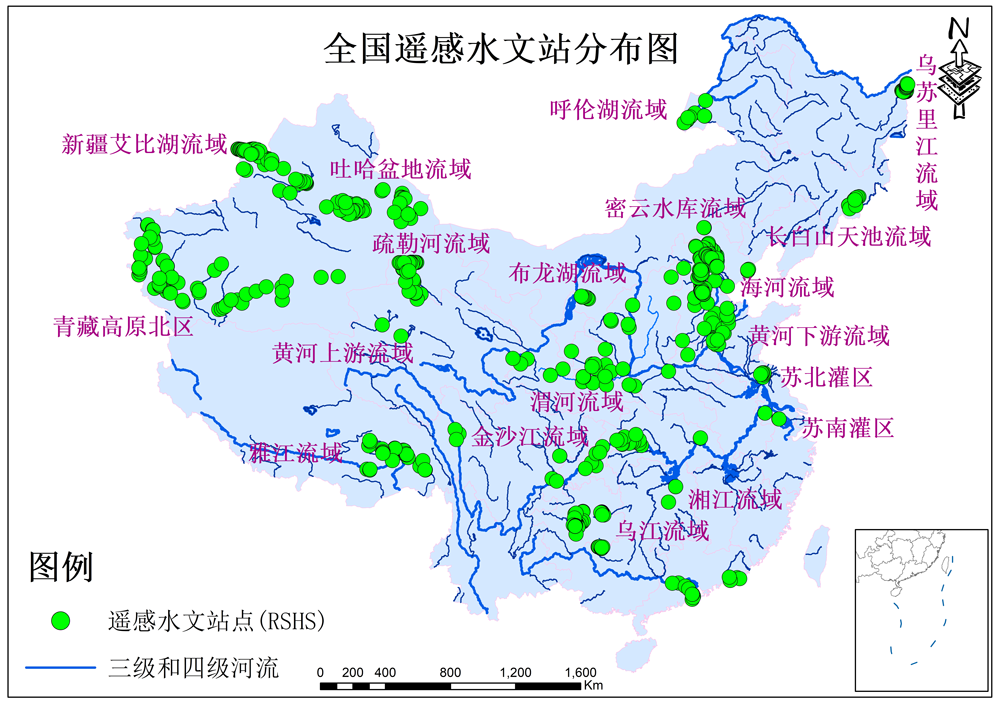
图2 全国遥感水文站分布图
5、已经取得理论成果和技术成果
a.理论成果:
1. Shengtian Yang, Zihao Pan, Hezhen Lou, Chaojun Li, Jun Zhang, Yujia Zhang, Yin Yi, Jiyi Gong, Ya Luo, Min Zhi, Xi Li. Reconstruction of the water cycle process reveals the 600-year evolution of the human-water relationship in Tunpu, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023,617(A).
2. Shengtian Yang, Baichi Zhou, Hezhen Lou, Zhengfang Wu, Shusheng Wang, Yujia Zhang, Zihao Pan, Chaojun Li. Remote sensing hydrological indication: Responses of hydrological processes to vegetation cover change in mid-latitude mountainous regions[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2022, 851(1).
3. Yang Shengtian,Li Chaojun,Lou Hezhen,Luo Ya,Wang Pengfei,Zhang Jun,Li Xi,Wu Xijin. The Impact of Urban Expansion on Plant Diversity Change in Karst Regions of Southwest China[J]. Chinese Geographical Science,2022,32(3).
4. Lou Hezhen,Zhang Yujia,Yang Shengtian,Wang Xuelei,Pan Zihao,Luo Ya. A New Method for Long-Term River Discharge Estimation of Small- and Medium-Scale Rivers by Using Multisource Remote Sensing and RSHS: Application and Validation[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(8).
5. Li Chaojun,Lou Hezhen,Yang Shengtian,Li Xi,Zhang Jun,Pan Zihao,Zhang Yujia,Yi Yin,Gong Jiyi. Effect of human disturbances and hydrologic elements on the distribution of plant diversity within the Shamu watershed, Mt. Yuntai Nature Reserve, China. [J]. Journal of environmental management,2022,311.
6. Wufu Adilai,Yang Shengtian,Chen Yun,Lou Hezhen,Li Chaojun,Ma Ligang. Estimation of Long-Term River Discharge and Its Changes in Ungauged Watersheds in Pamir Plateau[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(20).
7. Wang Juan,Yang Shengtian,Lou Hezhen,Liu Huiping,Wang Pengfei,Li Chaojun,Zhang Fei. Impact of lake water level decline on river evolution in Ebinur Lake Basin (an ungauged terminal lake basin)[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2021,104.
8. Wang Juan,Yang Shengtian,Liu Huiping,Wang Pengfei,Lou Hezhen,Gong Tongliang. Simulation of Lake Water Volume in Ungauged Terminal Lake Basin Based on Multi-Source Remote Sensing[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(4).
9. Shengtian Yang,Juan Wang,Pengfei Wang,Tongliang Gong,Huiping Liu. Low Altitude Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and Satellite Remote Sensing Are Used to Calculated River Discharge Attenuation Coefficients of Ungauged Catchments in Arid Desert[J]. Water,2019,11(12).
10. Zhang Xianlong,Zhang Fei,Qi Yaxiao,Deng Laifei,Wang Xiaolong,Yang Shengtian. New research methods for vegetation information extraction based on visible light remote sensing images from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2019,78.
11. Lou, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, S., Wang, X., Pan, Z., & Luo, Y. (2022). A New Method for Long-Term River Discharge Estimation of Small-and Medium-Scale Rivers by Using Multisource Remote Sensing and RSHS: Application and Validation. Remote Sensing, 14(8), 1798.
12. Lou, H., Scovronick, N., Yang, S., Ren, X., Shi, L., Fu, Y., ... & Luo, Y. (2021). A balance exists between vegetation recovery and human development over the past 30 years in the Guizhou Plateau, China. Ecological Indicators, 133, 108357.
13. Lou, H., Wu, X., Ren, X., Yang, S., Cai, M., Wang, P., & Guan, Y. (2021). Quantitative Assessment of the Influences of Snow Drought on Forest and Grass Growth in Mid-High Latitude Regions by Using Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 668.
14. Lou, H., Ren, X., Yang, S., Hao, F., Cai, M., & Wang, Y. (2021). Relations between Microtopography and Soil N and P Observed by an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Satellite Remote Sensing (GF-2). Polish Journal of Environmental Studies, 30(1).
15. Lou, H., Zhang, J., Yang, S., Cai, M., Ren, X., Luo, Y., & Li, C. (2021). Exploring the Relationships of Atmospheric Water Vapor Contents and Different Land Surfaces in a Complex Terrain Area by Using Doppler Radar. Atmosphere, 12(5), 528.
16. Yang, S., Li, C., Lou, H. (通讯), Wang, P., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., ... & Li, X. (2021). Role of the countryside landscapes for sustaining biodiversity in karst areas at a semi centennial scale. Ecological Indicators, 123, 107315.
17. Lou, H., Wang, P., Yang, S., Hao, F., Ren, X., Wang, Y., ... & Gong, T. (2020). Combining and Comparing an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle and Multiple Remote Sensing Satellites to Calculate Long-Term River Discharge in an Ungauged Water Source Region on the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing, 12(13), 2155.
18. Yang, S., Li, C., Lou, H.(通讯), Wang, P., Wang, J., & Ren, X. (2020). Performance of an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) in Calculating the Flood Peak Discharge of Ephemeral Rivers Combined with the Incipient Motion of Moving Stones in Arid Ungauged Regions. Remote Sensing, 12(10), 1610.
19. Yang, S., Wang, P., Lou, H.(通讯), Wang, J., Zhao, C., & Gong, T. (2019). Estimating River Discharges in Ungauged Catchments Using the Slope–Area Method and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. Water, 11(11), 2361.
20. Zhao, C.S., Zhang, C.B., Yang, S.T., Liu, C.M., Xiang, H., Sun, Y., Yang, Z.Y., Zhang, Y., Yu, X.Y., Shao, N.F. & Yu, Q. (2017). Calculating e-flow using UAV and ground monitoring. Journal of Hydrology, 552: 351–365. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.047)
21. Zhao, C.S., Yang, S.T., Zhang, H.T., Liu, C.M., Sun, Y., Yang, Z.L., Zhang, Y., Dong, B.E., & Lim, R.P. (2017). Coupling Habitat Suitability and Ecosystem Health with AEHRA to Estimate E-flows under Intensive Human Activities. Journal of Hydrology, 551: 470–483. (DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.05.047)
22. Zhao, C. S., Pan, T. L., Xia, J., Yang, S. T., Zhao, J., Gan, X. J., ... & Ding, S. Y. (2019). Streamflow calculation for medium-to-small rivers in data scarce inland areas. Science of The Total Environment, 693, 133571. (DOI:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.377)
23. 潘子豪,杨胜天,娄和震,于静洁,王忠静,张军.缺测站干旱流域生态输水遥感监测与农业节水效益分析[J].干旱区地理,2022,45(03):774-785.
24. 杨胜天,王鹏飞,王娟,娄和震,巩同梁.结合无人机航空摄影测量的河道流量估算[J].遥感学报,2021,25(06):1284-1293.
25. 王鹏飞,杨胜天,王娟,潘天力,章四龙,巩同梁.星-机一体的水力几何形态流量估算方法[J].水利学报,2020,51(04):492-504.
26. 潘天力,杨胜天,相华,赵长森,赵瑾.小型消费级无人机快速高精度估算地物高度[J].中国农业信息,2019,31(01):112-124.
27. 赵长森,潘旭,杨胜天,刘昌明,陈新,张含明,潘天力. (2019). 低空遥感无人机影像反演河道流量[J]. 地理学报, 74 (7): 1360-1376.
28. 张纯斌,杨胜天,赵长森,娄和震,张亦弛,白娟,王志伟,管亚兵,张远.小型消费级无人机地形数据精度验证[J].遥感学报,2018,22(01):185-195.
b.技术成果:
(1)软件登记:《基于遥感的多方法河道流量计算系统V1.0》,登记号:2019SR0973506。
(2)发明专利申请:《一种遥感水文站监测河流径流的方法》,目前处于二审审查阶段。
